What is a Carotid?
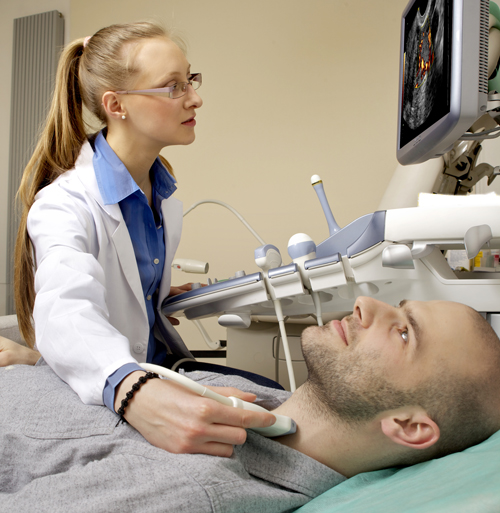
A carotid is a simple, safe non-invasive procedure to have done to diagnose (assess if you have) disease in the arteries of neck. The most common is plaque. There are no needles. You will lie on an examination table. You will tip you chin up with your head back and rolled to the right or left. The sonographer will hold a transducer (a device that resembles a computer mouse) against your neck, slowly sliding it up and down. Because the sound waves do not readily pass through air, a clear jelly-like substance is applied between the neck and the transducer to improve the contact of the transducer with the skin. The sonographer will apply this gel to your neck. Doppler evaluation of blood flow in the neck through the blood vessels is done at various times during the exam. Doppler technique measures the speed and direction of the blood flow within the arteries. It screens the arteries for abnormalities.
With Doppler echocardiograms, as the transducer moves over your neck you will hear a “whooshing’ sound much like that of a washing machine if the sonographer chooses to turn this function on. This sound relates to the movement of blood within your neck vessels. The test takes approximately 30 minutes to complete.
How does the carotid work?
Carotid ultrasound is a painless and harmless test that uses high-frequency sound waves to create pictures of the insides of your carotid arteries. You have two common carotid arteries, one on each side of your neck. They each divide into internal and external carotid arteries. The internal carotid arteries supply oxygen-rich blood to your brain. The external carotid arteries supply oxygen-rich blood to your face, scalp, and neck. Carotid ultrasound shows whether a waxy substance called plaque has built up in your carotid arteries. The buildup of plaque in the carotid arteries is called carotid artery disease. The transducer that’s placed on your neck sends sound waves toward the carotid arteries. Like the sonar on a submarine, the sound waves bounce off the arteries, and are collected by the transducer. Because it is only sound waves the procedure has no side effects. There is no radiation involved.
These returning sound waves are processed by a computer, assembled into a two-dimensional image of the beating arteries, and displayed on a TV screen (which you will be able to see depending on your position). By aiming the transducer, the technician will be able to image the important arterial structures.
Why is a carotid performed?
Your referring physician wants to determine if you neck arteries are plaque, thrombus and free of any other disease state. With the help of the sonographer and the different functions of the scanner the interpreting physician quickly assesses carotid patency and flows to determine acquired problems; if any. The causes for bruit (sound), effects of trauma (stroke), high blood pressure, assess for thickening of walls , following chronic conditions (e.g. kidney disease), and follow up after a surgical procedure are all reasons for having an echocardiogram.
Home Preparation for Carotid
– You may eat , drink and take your medications as usual
– If you wear a T shirt or a shirt with no collar you will not be required to remove your clothes from the waist up.